A course material reflects the knowledge domain, the users of the material, and the context in which it is to be used. Traditionally most material is produced in word processors and has a static form.
It is useful to create scenarios/synopsis (building a house,..) - themes (an exploration,...).
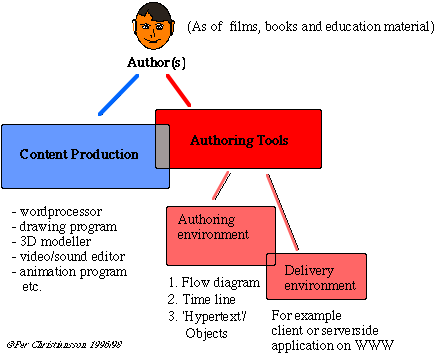
Authoring is often a teamwork between different competencies (HCI, conceptual modeling, pedagogics, incremental prototyping, ...)
Below are mentioned some of the authoring tools that exist today (runnable on both PC and Mac).
- Authorware (flow diagram type) from Macromedia http://www.macromedia.com/index.html
- Director (time line type). Also from Macromedia. (Director applications can be 'burned' and and stored on a server for downloading to clients. This requires a plug-in).
- Hyperstudio (Hypertext type) from Robert Wagner Inc. (now Knowledge Adventure). http://www.hyperstudio.com. The pioneering program in this field was HyperCard from Apple Computer around 1988.
- ToolBook (hypertext type only on windows) from Asymetrix Learning Systems Inc. http://www.asymetrix.com.
- FileMaker (Hypertext with database) from Filemaker Inc. (former Claris) http://www.filemaker.com.
- Macromedia Flash. http://www.macromedia.com/software/flash/. See an example at
http://www.evicom.se/.
- DreamWeaver (visual web layout tool) from Macromedia
See also 'Verktyg för multimediaproduktion' at
http://it.civil.auc.dk/it/reports/hm-kompendium/authoringtools.html (moved from KBS-Media Lab, Lund University).
A number of different domain knowledge experts, except from the domain under consideration, have to be present or available during the course development. Experts on,
- conceptual modeling of course material (writing of synopsis and storyboards, documentation of conceptual models, use of mind maps and flow charts),
- design of underlying data models and control structures,
- pedagogical models (e.g. project and problem based learning, story telling, simulation, physical experiments),
- human computer interaction, HCI, navigation and search metaphors, cognitive overhead (lost in hyperspace),
- cognitive psychology,
- human communication,
- system integration and networking,
- graphic design and image editing,
- scenario design and dramaturgy,
- animation,
- video production and editing,
- midi, musical instrument digital interface, and (multi channel) sound editing,
- desk-top publishing (layout, reading rhythm, fonts, etc.)
- evaluation models,
- requirements formulation,
- incremental prototyping and demonstrator development.
Further references
- Anark Studio. http://www.anark.com/products/anarkstudio.htm