|
IT Tools - Virtual Buildings
IT i Civilingeniørspeciale i Byggeledelse/IT in Building Management. 2003
1. Background
[goto top]
Since the introduction of the world wide web (WWW) and standardisation of Internet services and communication protocols we can see a huge shift in the way we communicate, collaborate and handle digital knowledge. The semester 7 course focuses on models and representations of building products and processes. (In the semester 8 course we take an end user perspective on how ICT tools can support collaboration, communication and access to Internet based computer resources.)
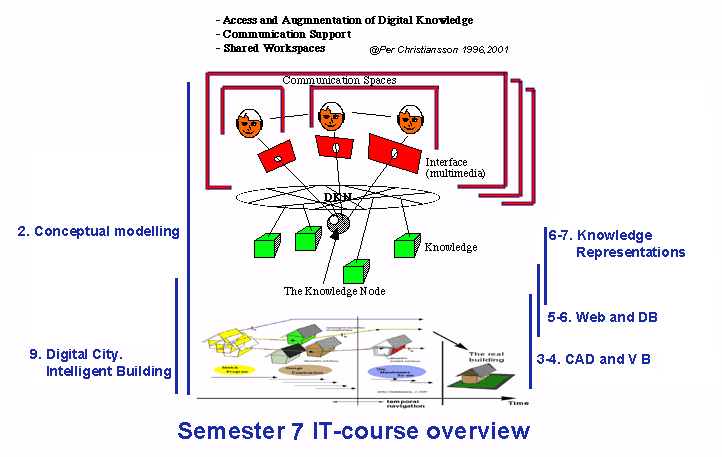
The anticipated ICT tools are only partly developed and must be designed tested and implemented in close collaboration with the building process end users. This requires that civil engineers get a deeper understanding of some knowledge domains that up till now only has been partly covered in the civil engineering curricula.
The ICT will strongly influence how we take advantage of and interact with the computer resources
- information storage and interaction media will be more separated (paper is both)
- it will be easier to adapt information containers to user needs and usage context (meta data, models interoperability, model access, etc.)
- the web will form the infrastructure for information container access, and application communication
- human collaboration, team work and communication modes will be developed and partly changed
- collaboration work spaces will get a added virtual dimension being less dependent of the physical room.
The mutual influence between practice and ICT progress is necessary to maintain. Civil engineers must posses both general and some specialised ICT related knowledge to be able to specify and participate in the development of new ICT tools and to be pro-active in the process of changing work routines and company and project organisation.
This course aims at providing general knowledge on how
present and future digital product and process models can be designed and implemented as well as deeper knowledge in certain key areas such as web-database integration, the semantic web, virtual building models, analyses/simulation program communication with product models, and intelligent and responsive buildings.
2. Goal
[goto top]
The goal of the 'IT
in the Building Process - The Virtual Building' course is to mediate knowledge
about fundamental concepts, technologies and methods to analyse and develop
models which describes a building, the building process and the digital
infrastructures from design to application as well as mediation of knowledge about how the future services, systems, and infrastructures for knowledge management can be built and integrated.
3. Volume/Placement
[goto top]
This 2 modules course is one of 2 with emphasis on IT during the semester 7 Master of IT in Building Management education
(calendar).
4. Content
[goto top]
Explaining Knowledge Management.
Knowledge Management tools. Principles for meta-structuring in web based
structures. Project webs. Properties of the next generation Semantic
Web. (XML, RDF).
Knowledge
representations in practice.
Web database integration.
Existing classification systems and meta classification methodologies.
Conceptual and data modelling techniques.
Acquisition and storage of building process data. Design and development
of services for knowledge transfer and knowledge management.
Introduction to conceptual modelling methods and languages.
Building Product Models in perspective.
Cad system properties.
Building applications supported by product models.
Building 3D models for the Web (Virtual reality mark-up language - VRML,
and Cult3D).
Future structures of virtual building models.
International Foundation Classes, IFC.
IT infra structures and intelligent buildings
5. Learning Material
[goto top]
The course content is delivered through the lectures, reading of literatur , and exercises/miniproject. It is impossible to find a set of literature that covers the course content completely. The lectures are supported by lecture slides available on the course web site. The slides with emphasized titles in the navigation bar has the same status as course literature (though not eventual references on the slide).
References to further reading is found in the lecture notes.
The coarse literature consists of both Lecture Slides and literature according to the list below.
The 'IT in Civil Engineering' site (http://it.civil.auc.dk/) also gives access to
previous years courses and if applicable mini projects. You reach it from the top of this page.
5.1 Lectures
[goto top]
The lectures are accessed from the lecture scheme below.
Each lecture has a easy to navigate slide bar and an opening slide with
short content description, questions for self assessment, references to the literature according to the literure list below and proposals for further reading.
The four hour lecture/exercise followes the scheme
- 1 hour lecture
- 1 hour exercise in group
- 2 hours exercise results presentation and follow discussions
5.2 Exercises/Mini-project
[goto top]
The exercies are also accessed from the lecture scheme below.
The exercices may well take use cases from the ongoing semester project or even be contained in a mini-project defined by the group.
The following domains will be covered during the exercices
- Write scenario(s) of the future ICT supported building process
- Conceptual modelling of your semester 7 project
- Building and handling IFC based product models and components
- Database design and web access
- Meta structuring of information using XML and RDF
- new services in digital cities and intelligent buildings
-
-
5.3 Software
[goto top]
The following ICT, Information and Communication tools, are available during exercises/minproject activity. (those marked with * only at the Media Lab at institute 6)
- AutoCad ADT
- ArchiCad
- Solibri
- XML Spy
- ......
- Adobe Acrobat Distiller and Exchange to produce interactive PDF documents
- Groove, Netmeeting, and Yahoo Messanger to establish shared workspaces
-
5.4 Literature
[goto top]
|
/1/
|
Phiri T, 1999, "Information Technology in Construction Design". Thomas Telford Ltd, London. (227 p.). (Extracts):
Historic background reading 'Systems software. Application software' (pp. 12-18), 'Time and project management activities' (pp. 27-33), 'Data manipulation and mathematical analysis' (pp. 47-51), CAD/CAM/CAE and multi-media' (pp. 52-67).
Case studies: 'Anthony Hunt Associates, Structural and Civil Engineers' (pp. 87 - 91), 'Battle McCarthy, Consulting Engineers' (pp. 97-100), 'BDP Ltd, Architects, Engineers and Surveyors' (pp. 101-108), 'DEGW, Architects, Space Planning and Management Consultancy' (pp. 122-127), 'Price & myers, Consulting Structural and Civil Engineers' (pp. 177-180),'Reiach & Hall, Architects' (pp. 181-184), 'Richard Rogers Partnership, Architects' (pp. 189-194), 'SOM, Architects' (pp.195-201).
'Conclusions and future developments' (pp. 203-211). (TOTAL extract 88 pp.)
|
|
/2/
|
Rasmussen Annelise, 1996, "Introduktion til IDEF0 Version 1.1". Institut for Anvendt Konstruktion og Produktion. Danmarks Tekniske Universitet. Lyngby (30 pages)
|
|
/3/
|
Christiansson, P, 2001, "Capture of user requirements and structuring of collaborative VR environments". AVR II & CONVR 2001.
Conference on Applied Virtual Reality in Engineering & Construction Applications of Virtual Reality. Gothenburg October 4-5, 2001. (17
pp.)
|
|
/4/
|
Langt gangsprojektet (Master thesis Building Management) "Anvendelse af metadata i byggeprocessen" (Use of Meta Data in the Building Process). Jakob Brøndsted, Kim Larsen, 2001/2002.
[Appendix 2 page 253-270]
|
|
/5/
|
"GDL Object Technology. Enhancing the Information Process in the Building Industry". GDL Technology. [8 pp.]. http://www.gdltechnology.com/,
http://www.gdlcentral.com/.
|
|
/6/
|
Liebich T, 2001, "IAI IFC. Concept of the IFC Standard
and the relation to ISO & XML". Interop in AEC&fm, Sydney, Australia, 29-30.10.2001 (26 pages).
|
|
/7/
|
Christiansson P., Da Dalto Laurent, Skjaerbaek J. O., Soubra S., Marache M., 2002, "
Virtual Environments for the AEC sector - The Divercity experience
European Conference of Product and Process Modelling. eWork and eBusiness in AEC.
9-11 September 2002, Portoroz, Slovenia. (8 pp.)
KEYWORDS: Virtual Environments, Collaborative Work, Virtual Workspace, 3D Real Time Interaction, Construction Industry.
|
|
/8/
|
Pedersen S, 2002, "Databasestyrde websider". IDG Forlag, Valby. (87 pp.). [69 DKK].
|
|
/9/
|
Christiansson P, Herrera A, 1987, "Kunskapsbaserade system/expertsystem. Värdering av några existerande verktyg" / "Knowledge Based Systems/Expert systems.
Evaluation of some existing tools". NBS-DATA seminarium, Oslo, 24-25 september 1987. (15 pp).
|
|
/10/
|
Johnson, M., 1999, "XML for the absolute beginner".
http://www.javaworld.com/javaworld/jw-04-1999/jw-04-xml.html
|
|
/11/
|
van Grieken K, 2002, "TCP/IP in Building Management Systems. The network Technology for Today and Tomorrow". AutomatedBuildings.com.
(local copy)
|
|
/12/
|
Gray E, 2000, "Achieving Control System Independence. Controls, Computers and Standards". AutomatedBuildings.com.
(local copy)
|
|
/13/
|
Falk V, "LON i dagens Danmark". Dansk Automationsselskab.
|
|
/14/
|
Christiansson P, 2000, "Knowledge Representations and information Flow in the Intelligent Building". 'TProceedings of he Eighth International Conference on Computing in
Civil and Building Engineering. ICCCBE-VIII 2000 (eds: Fruchter R, Pena-Mora F, Roddis K)', ISBN 0-7844-0513-1. American Society of Civil Engineers, Reston, Virginia, USA. (Stanford University, USA. August 14-17, 2000). (pp. 604-611).
KEYWORDS: intelligent building, services, digital city, design, communication
|
|
/15/
|
Solibri Inc., 2002, "Getting Started with Solibri Model Checker" (24 pp).
|
6. Examination
[goto top]
Oral test based on 1-3 hour discussions a group on a mini project or exercises collection. Assessed with the grade "passed" or "failed" with internal
censor participation.
Examination will take place at Fib.14/58, Wednesday January 14,
2004, at 09.00 (Group 2.122), 10.00 (Group 2.124 and 11.00 (Group 2.121). Examinators are Per Christiansson and Kjeld Svidt, censor NN NN.
The group exercises/miniproject reports and presentation at examination are presented
here
- Group 2.121
- Group 2.122
- Group 2.124
Please fill in the course evaluation form.
7. Course Participants
[goto top]
7.1 Students
Gruppe: 2.121
Projekt:
Carl Christensen & Co
|
Per Bay Petersen
Kræn Lau Andersen
Kasper Abildgaard
Subaranjini Panneerselvam
Lars Rocatis Nielsen
Frederikke Beck
|
Gruppe: 2.122
Projekt:
Kastrup Vinduet
|
Jakob L. Poulsen
Kim Christensen
Uffe Nybo Mortensen
Connie Schultz Højbjerg
Karen Elvang Svendsen
|
Gruppe: 2.124
Projekt:
Gandrup
|
Jeanette Noer
Vibeke Larsen
Sebastian Gerschefski
Tim Krøyer Madsen
Marie Louise Sørensen
Michael Nygaard Schang
|
7.2 Teachers
Prof Per Christiansson (course responsible) , Asst. Prof. Kjeld Svidt. , PhD Student Mads Carlsen.
8. Lecture Scheme
[goto top]
1
Wednesday October 22, 2003
8.15 -12.00
Fibigerstræde 14,
room 59
Aalborg University
(Per Christiansson)
|
|
SETTING THE SCENE
This lecture explains and comments the
introduction of IT in the building process during the
latest decades.
Digital models, standards and systems have been developed to support
for example engineering
calculations, stability analyses, simulations, graphic
presentations, time planing, resource management,
and documentation.
Building product and process models are explained and exemplified as well as
relevant knowledge management issues.
|
|
Literature
/1/
Exercise A
|
2
Thursday October 23, 2003
8.15 -12.00
Fibigerstræde 14,
room 59
Aalborg University
(Per Christiansson)
(Mads Carlsen)
|
|
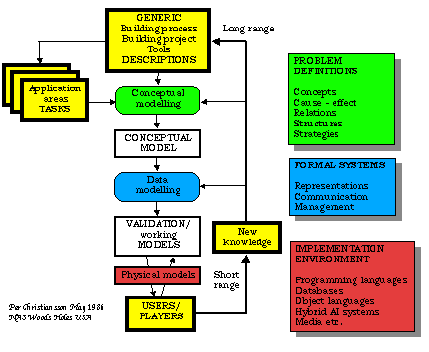
Conceptual Modelling
Before we arrive to the actual implementation of our data
models in computer systems we must make so called
conceptual models.
A conceptual model is a high level description of parts of and the
whole process we are considering for computer application.
It will help us to understand and describe the world we
are dealing with (even if we do not intend to make a
computer implementation). There are different conceptual modelling
methods which are suited for different or similar
application areas.
We will look at conceptual modelling of the building product and
it's time dependent properties (process models) during
specification, design, contruction, use,
and demoltion/recycling of the building product.
We will in more detail study some conceptual modelling metohods and
also mention the so called Contectual Design method
for capture of user requirements and user enviroenment design in connection
with system development.
|
|
Literature
/2/,/3/
Exercise B
|
3-4
Thursday October 30, 2003
Thursday November 6, 2003
8.15 -12.00
Sohngaardsholmsvej 57, Room C-119
Aalborg University
(Kjeld Svidt)
|
|
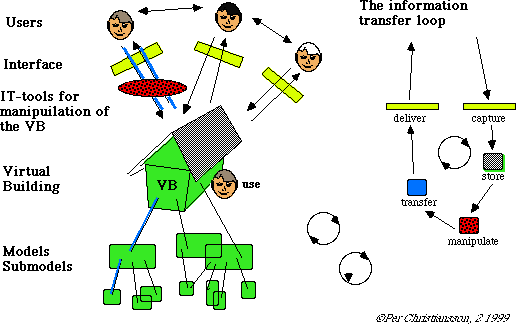
CAD AND VIRTUAL BUILDING MODELS
Building products and processes must be described in
formalised data models before than can be implemented
in computer systems.
An overview of attempts to make digital building models is given and commented on. The first models were made during the 1960'ies in key system fashion. We will look at the properties of the latest three decade building models and what we can expect in the future.
An overview is given over efforts and results in the
area of (de facto) standards development for formalised
descriptions which can be used in
building product models, building process
models, EDI - Electronic Data Exchange, vendor
building components models, and knowledge managements
models.
Special emphasis is on the the development of standardised International Foudation
Classes (IFC) to describe building objects.
We will also study different Cad systems and their ability to handle standardised
information. AutoCad, ArchCad, Revit and the DIVERCITY framework (EU project 2000-2001).
|
|
Literature
/4/, /5/, /6/, /7/, /15/
Exercise C
|
|
5-6
Thursday November 20, 2003. Fibigerstræde 14,
room 59, Aalborg University.
8.15 -12.00
(Per Christiansson)
(Kjeld Svidt)
(Mads Carlsen)
Monday November 24, 2003. Fibigerstræde 16,
Aalborg University, room 1.211.
12.30 - 16.15
(Mads Carlsen)
|
|
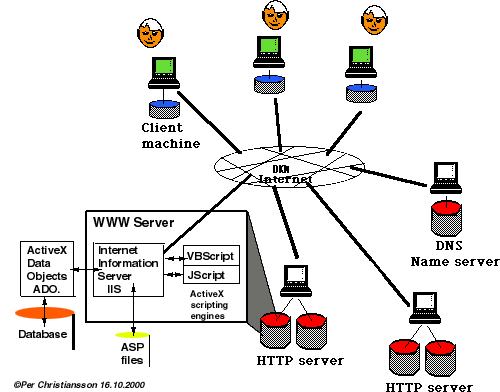
WEB AND DATABASES
Relational databases is and will be an very important information container
for building process and product information.
We will repeat some database basics from semester 6 (normalisation, SQL calls
to databases).
We will also learn about the principles and methods behind connecting databases to web browsers.
|
|
Literature
/8/
Exercise D
|
7-8
Thursday November 27, 2003
Fibigerstræde 14,
room 59, Aalborg University
Tuesday December 2, 2003
12.30 -16.15
Fibigerstræde 14,
room 59, Aalborg University
(Per Christiansson)
(Mads Carlsen)
|
|
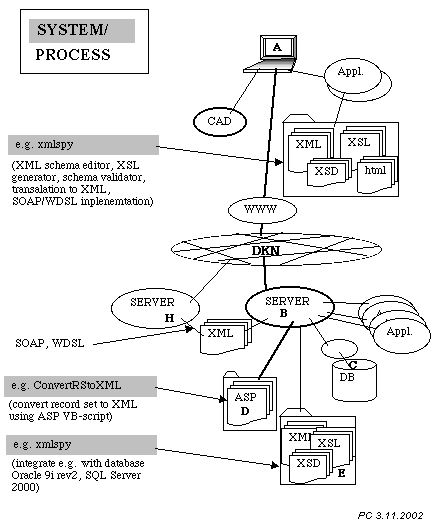
KNOWLEDGE REPRESENTATIONS (HTML, XML)
Computers can be used to store information which
will mimic or support our own knowledge stored
in hour brains. There is a spectrum of different
computer software which can be used
to represent different knowledge handling routines
and knowledge domains. For example in connetion with
decision support, information retrieval and storage,
experience capture, collaboration, and design syntheses.
We will look at the following computer stored knowledge
representations - hypertext, relational databases,
We will focus on relational databses (see 5-6. Web and Databases) and hypertext representations supported by HTML (with recap of
HTML basics) and the new ways we have to separate content and access of
web based hypertext information (XML, XSL).
You will also get a short insight into other representation forms such as
production
systems, predicate logig based systems, artificial neural networks, induction systems, and analogue
representations (Object representations are covered in another
course and will only be touched upon here). We will also in this
connection comment on knowledge acquisition methods.
We will during lecture 8 dive deeper into the
principles for meta-structuring of web based information
containers (URIs) in web based environments. Project webs and properties of the next generation Semantic Web (XML, RDF) and how applications can use XML as a transport
format will be described. The relational database example will be used (XSQL).
|
|
Literature
/9/, /10/
Exercise E
|
9
Thursday December 4, 2003
8.15 -12.00
Fibigerstræde 14,
room 59, Aalborg University
(Kjeld Svidt)
(Per Christiansson)
|
|
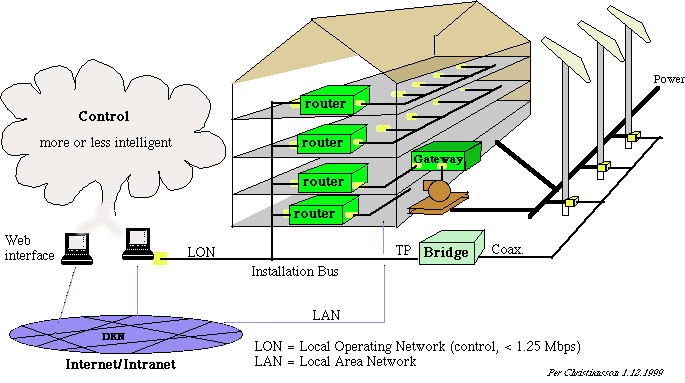
9. THE DIGITAL CITY AND SOCIETY.
THE INTELLIGENT BUILDING
Information technology,IT, will cause a paradigm shift in
our society from the art of writing, printing to the art
of communication.
In the same way as the car highly influenced the physical
design of our society IT will higly influence the forming
of the global villages.
New services will be designed and implemented in the
citizen nets to support
the village inhabitants - access to services and
facts bases, and possibilities for active participation in
the (democratic) decision process.
We will study and analyse ongoing efforts in the area.
The building product itself will contain or have attached
to it IT-tools which will support it during it's life
time. Information handling and communication support
will be given for the building inhabitants,
for the adminstration of the building and it's operation and maintenence
(O&M). The IT support will be in the form of conventional computer systems and sophisticated input/output units as well as in the building
and installations embedded computer systems.
We will investigate exisiting and expected infrastructures,
systems, and services in the intelligent buildings and digital cities,
and how they can be designed, modelled, and implemented.
|
|
Literature
/11/, /12/, /13/, /14/
Exercise F
|
10
[Thursday December 11, 2003]
NEW DATE
Tuesday January 13, 2004
08.15 -12.00
Fibigerstræde 16,
room 1.208
Aalborg University
(Per Christiansson)
(Kjeld Svidt)
(Mads Carlsen)
|
|
Literature
/xx/, /xx/
Fill in course evaluation.
|
[goto top]
|
|






